Human musculature and internal organs Stock Photo Biology Diagrams Muscle tissue is composed of cells that have the ability to shorten/contract in order to produce movement. The muscle cells, also called muscle fibers are long and slender. They are arranged in bundles or layers that are surrounded by connective tissue. Actin and myosin are the main contractile proteins in muscular tissue. There are three types of muscle in the body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. As with any muscle, the smooth, involuntary muscles of the visceral muscle tissue (which lines the blood vessels, stomach, digestive tract, and other internal organs) are composed of bundles of specialized cells capable of contraction and relaxation to create movement.
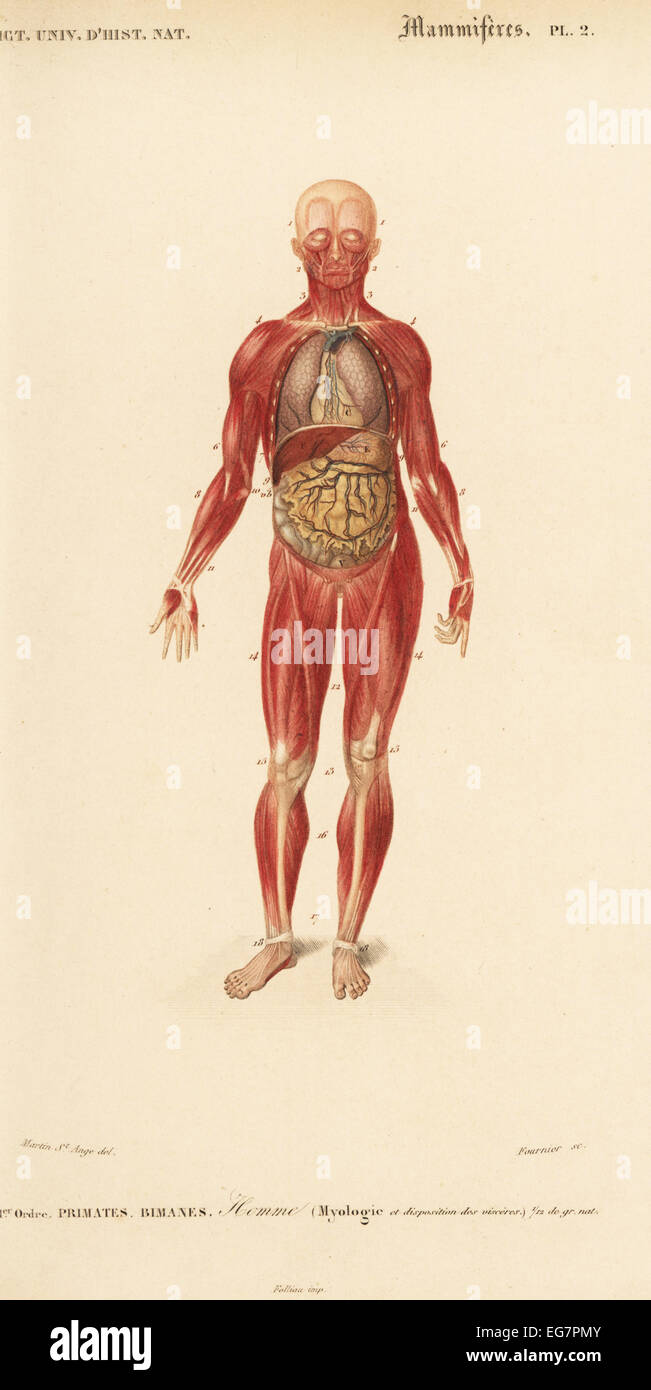
There are 12 major anatomy systems: Skeletal, Muscular, Cardiovascular, Digestive, Endocrine, Nervous, Respiratory, Immune/Lymphatic, Urinary, Female Reproductive, Male Reproductive, Integumentary. Muscular System The muscular system is responsible for the movement of the human body.
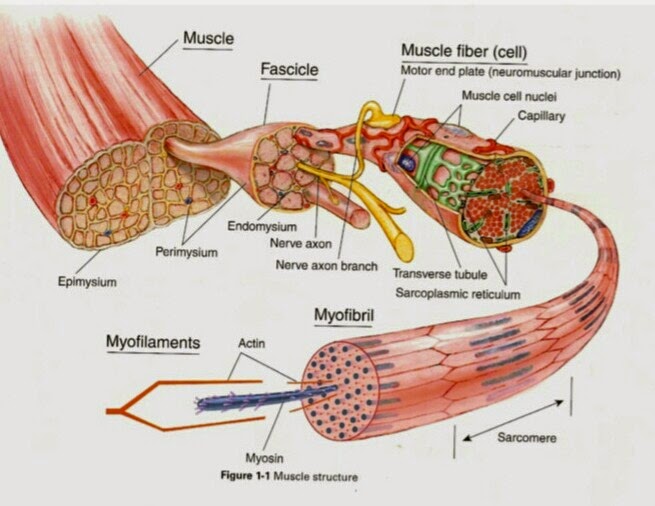
Interactive Guide to the Muscular System Biology Diagrams
The Muscles of the Human Body Muscles are essential components of the human body, enabling movement, maintaining posture, and performing a variety of vital functions. Understanding the structure, properties, and classification of muscles is fundamental for studying human biomechanics, physical activity, and exercise science. General Information About Muscles Muscles are soft tissues composed
Muscle is one of the four primary tissue types of the body (along with epithelial, nervous, and connective tissues), and the body contains three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle (Figure 33.1).All three muscle tissues have some properties in common; they all exhibit a quality called excitability as their plasma membranes can change their electrical Learn about the three types of muscle as you use our 3D models to explore the anatomical structure and physiology of human muscles. And don't worry, we'll explain the naming of skeletal muscles, too. Active muscles break glucoses off of glycogen molecules to provide an internal fuel supply. When muscles run out of energy during either human muscle system, the muscles of the human body that work the skeletal system, that are under voluntary control, and that are concerned with movement, posture, and balance. Broadly considered, human muscle—like the muscles of all vertebrates—is often divided into striated muscle (or skeletal muscle), smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.Smooth muscle is under involuntary control and is

3D Human Anatomy: Explore Interactive Models for In Biology Diagrams
These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Skeletal muscles have three layers of connective tissue (called "mysia", singular: "mysium") that enclose it and provide structure to the muscle as a whole, and also compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle (Figure 6.2).
