Dip History Photographic Exhibit Biology Diagrams In general, food webs with low biodiversity are more vulnerable to changes than food webs with high biodiversity. In some food webs, the removal of a plant species can negatively affect the entire food web, but the loss of one plant species that makes up only part of the diet of a herbivorous consumer may have little or no effect. Calves: They rely on their mother's milk for the first few years, gradually transitioning to solid food. Adults: Mature dolphins have a broader diet, perfected hunting skills, and can tackle larger or more elusive prey. Dolphin's Role in Marine Food Chain. Understanding the diet of dolphins isn't just about knowing what they eat.

The dolphin food chain interacts with various marine species. They primarily prey on fish, squid, and other marine invertebrates. However, they are also prey for larger predators such as sharks and orcas. This complex web of interactions highlights the importance of dolphins within the marine ecosystem and raises awareness of the need for

What is the food chain of a dolphin? Biology Diagrams
In a dolphin's food chain, primary consumers consist of small fish, crustaceans, and squid — animals that can be captured by dolphins with little effort. These animals exist in abundance near coastal areas where dolphins can find them easily and acquire substantial protein needed for growth and development. Some species of dolphins may even
swam up and ate the dolphin we had pegged to be at the top of this food chain," Young explained. A pod of vagrant killer whales known as orcas—the largest species of dolphin—made a brief

Dolphins and Coral Reefs Biology Diagrams
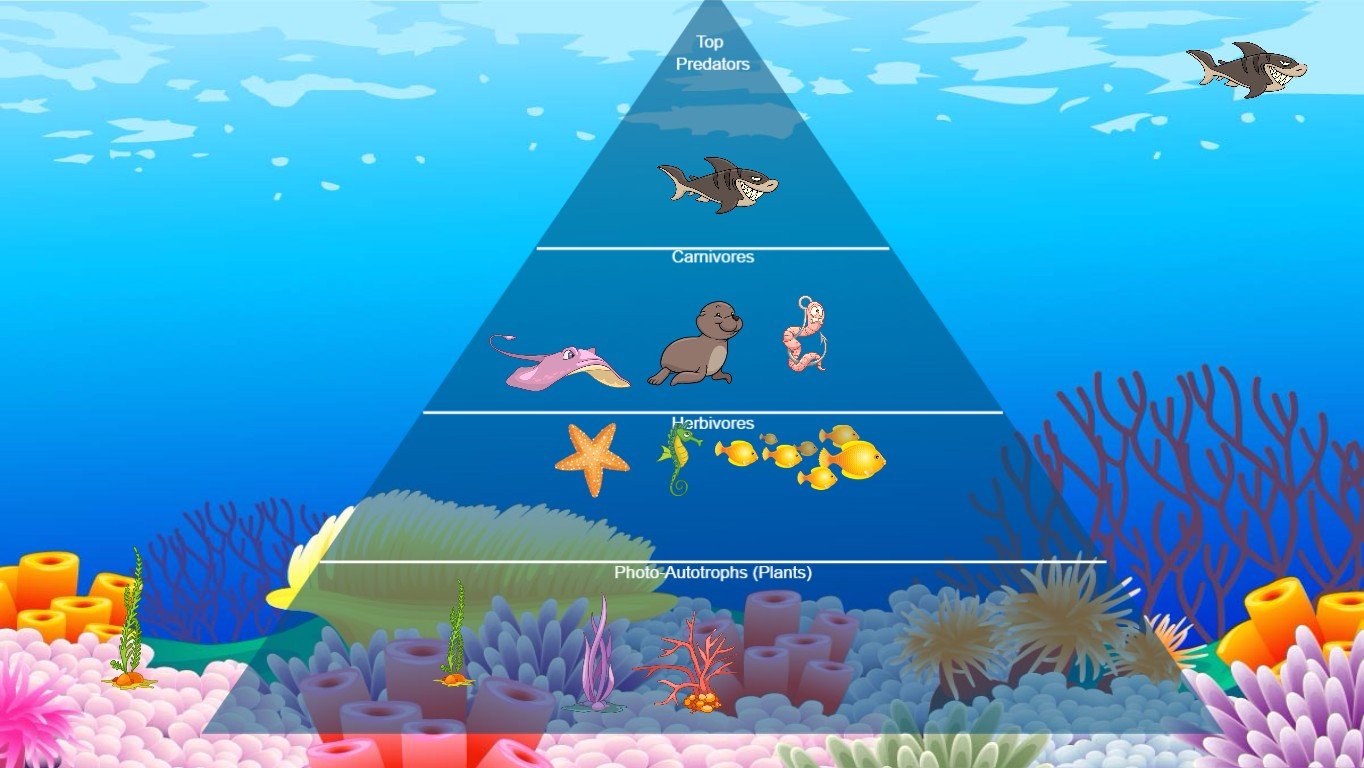
Coral reefs are vitally important to the health of all oceans. Corals are a source of primary production, which is the base of the seas' food web. Reef habitats are important in cycling nutrients and water quality, which are important to all species from the smallest plankton to the largest whales. A two-toned Atlantic Spotted Dolphin foraging.
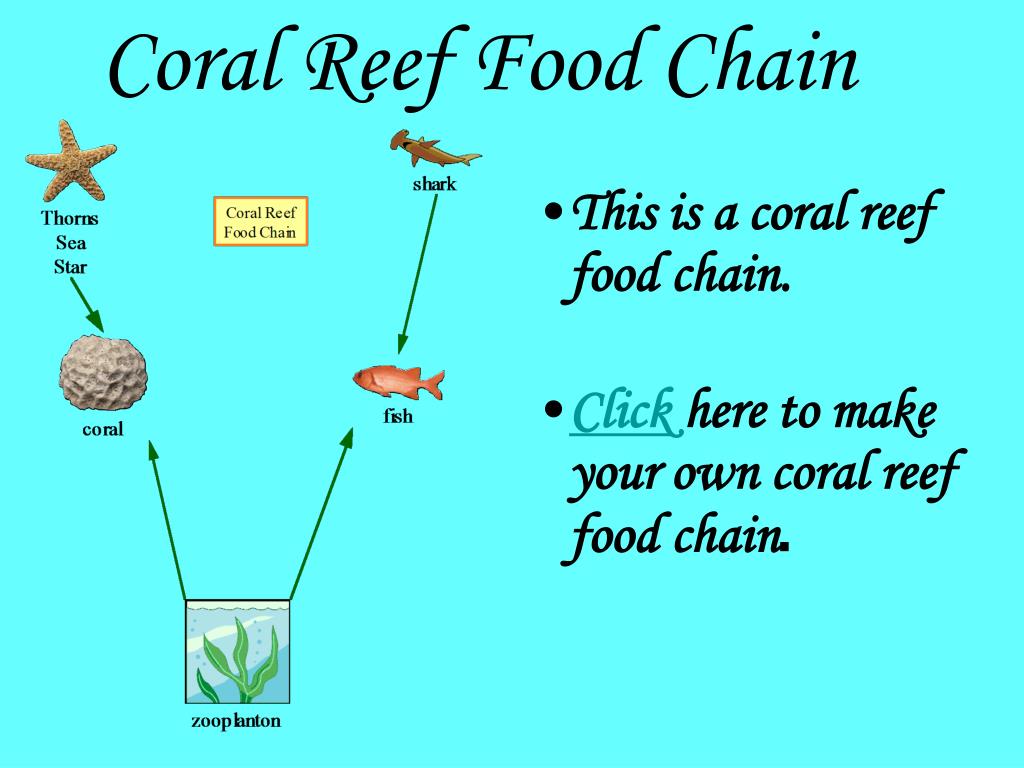
The Dolphin Food Chain: A Deep Dive into Marine Ecology. The dolphin food chain is a complex web of interactions within marine ecosystems, positioning these intelligent creatures as significant predators. Dolphins, being carnivores, primarily occupy a high trophic level, meaning they feed on other animals.Their position is defined by what they eat and what eats them. The dolphin food chain forms a vital part of the intricate marine ecosystem. Primary producers, such as algae, provide the foundation by converting sunlight into energy. Small fish and zooplankton consume these producers, while larger fish and squid hunt them. Dolphins, as secondary consumers, prey on these carnivores. Apex predators like sharks and killer whales hunt dolphins, completing the
